Rely on NovoSeven® RT—it is proven effective to treat GT when platelets don't work at home. Clinical trials show it controls bleeds in a majority of GT-related bleeds, and in surgical procedures.
Controls bleeds, wherever and whenever they happen.
Bleed control seen in clinical trialsa
Bleeding episodes
266 episodes
All treatmentsb
Surgical procedures
160 procedures
All treatmentsb
Effectiveness in childrena
- 94% bleed control in patients 0 to 12 years
- 100% bleed control in patients >12 to 16 years
aEffectiveness seen in a prospective, observational, multinational study (from an analysis of published cases and people who took part in trials and registries).
bNovoSeven® RT only and NovoSeven® RT with platelets and/or antifibrinolytics.
Stay prepared for bleeds
Did you know that identifying bleeds quickly is important? Learn the signs and symptoms of bleeds so you can identify them when and where they happen.
Safety supported by clinical experience.
NovoSeven® RT is a recombinant product, meaning it is made without human blood or plasma. This minimizes the possibility of viral contamination. NovoSeven® RT is the only recombinant therapy indicated for GT.c And its safety is supported by real-world evidence, with a <0.2% rate of unexpected blood clots reported.d
Serious blood clots that form in veins and arteries with the use of NovoSeven® RT have been reported.
cIn patients with refractoriness to platelet transfusions, with or without antibodies to platelets.
dThrombotic events reported for people with GT based on registry data collected.

Fast to infuse.
NovoSeven® RT provides low infusion volume, so infusing takes 2 to 5 minutes.e NovoSeven® RT is given as an intravenous (IV) bolus injection.
eAdminister as a slow bolus injection over 2 to 5 minutes, depending on the dose administered.
NovoSeven® RT (90 mcg/kg)

Meet Cathy.
She chooses NovoSeven® RT because it fits her lifestyle.
Goes where you go.
NovoSeven® RT is portable and travel ready, with compact packaging that’s easy to pack in a carry-on or backpack. And because it’s room temperature stable up to 77 °F, there’s no need to refrigerate.f
fNovoSeven® RT should be stored between 36 °F and 77 °F.
For complete storage information, please see Prescribing Information.

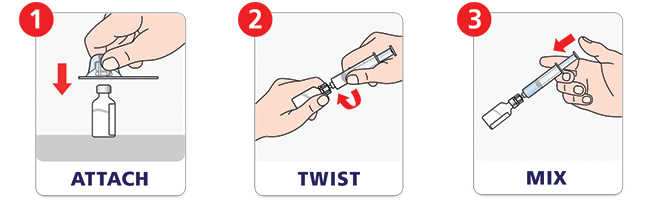
Quick to mix.g
NovoSeven® RT with MixPro® makes mixing a dose as easy as attach, twist, and mix. The prefilled syringe saves time—there are no extra steps to fill a syringe with diluent.
After mixing, NovoSeven® RT may be stored at room temperature in the vial for up to 3 hours.h
gCompared with mixing using histidine vials.
hFor complete storage and handling instructions, please see Prescribing Information.
What if I need surgery or a procedure?
We understand that you have concerns about controlling bleeds if you ever need surgery or a procedure. The good news is that NovoSeven® RT prevents bleeds during and after surgery and procedures in people with GT.
Talk to your doctor for more information on the surgical use of NovoSeven® RT.
About Glanzmann’s thrombasthenia (GT).

What is GT?

There are proteins on the platelets that help your blood clot properly. One type of these proteins is a glycoprotein called IIb/IIIa, which helps platelets connect to each other. Those platelets stick together to form a "plug" that stops a bleed. Someone with GT has specific defective glycoprotein IIb/IIIa. This means the platelets cannot form a plug to stop a bleed.

Who gets GT?

GT is a rare genetic disorder that affects about 1 in 1 million people. It is inherited from both parents and can occur in both men and women.

What are the signs of GT?

Those with GT mainly have skin and mucous membrane types of bleeding. The most common signs of GT include:
- Easy bruising
- Bleeding from the nose or gums
- Heavy menstruation
Other signs and symptoms include:
- Excessive bleeding after trauma or surgery
- Excessive bleeding after dental extractions

What are some treatments for GT?

One treatment option for GT is platelet transfusion; some patients who receive platelet transfusions may develop antibodies and become resistant. You may be able to use a bypassing agent to control your bleeds if platelets do not work for you.


Hear from people who
share your experience.
New to treatment? It’s
easy to get started.
![Icon: 5-step purification process of NovoSeven® RT (Coagulation Factor VIIa [Recombinant])](/content/dam/novonordisk/novoseven/cta/CTA-recombinant.jpg)
![NovoSeven® RT (Coagulation Factor VIIa [Recombinant])](/content/dam/novonordisk/novoseven/global/logo-novoseven-rt.png)

